
Smarter Support With Agentforce
Customer service is changing quickly. People expect answers right away, whether they are asking about a product, checking an order, or solving a technical issue. Relying only on human agents often means longer wait times and higher costs. A Salesforce Support Agent solves this by handling common requests, giving clear answers, and passing complex cases to the right person.
With Agentforce, Salesforce lets you build AI agents that work in Service Cloud to handle support tasks like FAQs, case creation, or routing complex issues to the right person. These agents connect to your data, knowledge, and workflows so customers get fast and accurate help. Plus, Agentforce isn’t limited to Service Cloud, it can serve on portals, messaging channels, and internal apps too, making it a versatile tool across your Salesforce ecosystem.
Insight:
Most customers expect fast, seamless support. Did you know that 77% want immediate interaction when contacting a company, and 70% expect every representative to already have their information? This shows that businesses need systems, like Salesforce Agents, that can provide instant responses while keeping customer data consistent and accessible across channels.
In this article, we’ll explore Agentforce Service Agent: what it is, its key capabilities, how to set it up, best practices for getting the most out of it, and common pitfalls to avoid. We’ll also cover real-world use cases and FAQs so you can see exactly how Agentforce fits into modern customer support operations.
- What Is a Salesforce Customer Support Agent
- Key Capabilities of a Support Agent
- Plan Your Support Actions Before Building Your Agent
- How to Create a Support Agent in Salesforce
- Best Practices for Building a Support Agent
- Troubleshooting and Common Pitfalls
- FAQs About Agentforce Support Agents
- 1. How do I know if my agent is performing well?
- 2. Can I change the agent’s behavior after deployment?
- 3. What should I do if the agent gives incorrect answers?
- 4. How do I test the agent before going live?
- 5. How can I make the agent easier for customers to use?
- 6. How to build a Success Agent in Salesforce?
- Conclusion: Building and Maintaining a Salesforce Agent
What Is a Salesforce Customer Support Agent
A Customer Support Agent or Agentforce Service Agent is a digital assistant in Service Cloud that helps customers get answers and complete simple tasks without waiting for a human agent. It can share knowledge articles, guide users through troubleshooting, create or update cases, and check request status.

The purpose of the Success Agent Salesforce or the Salesforce Sales Agent is not to replace people but to handle repetitive work so service teams can focus on complex issues. These agents are built with Agentforce, which connects company data, workflows, and records to conversations. This makes the Support Agent more than a basic chatbot, it becomes a reliable extension of the service team.
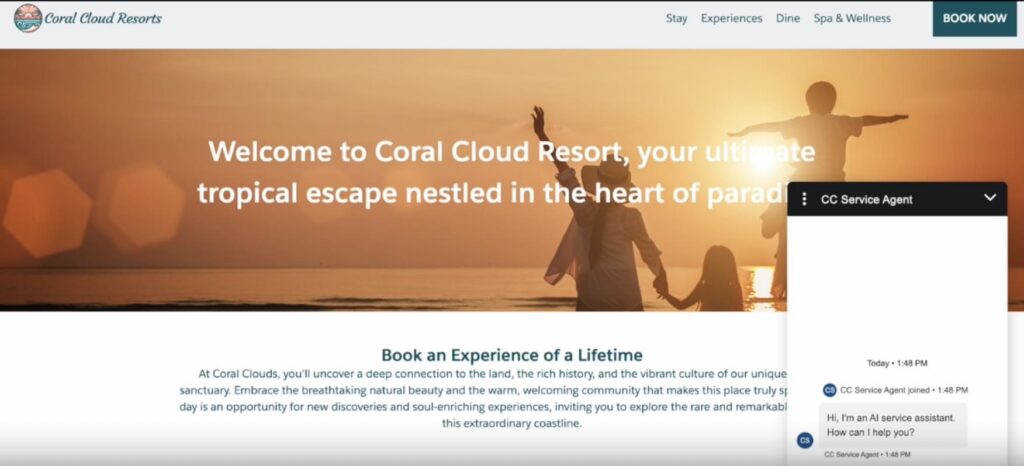
Why Build a Salesforce Support Agent
Customer expectations have changed. People want quick answers at any time, whether it’s a simple “how do I reset my password?” or checking the progress of an order. Service teams often spend most of their time on these routine requests, leaving less space for handling complex problems. An Agentforce Support Agent can take on this first layer of work, giving customers instant replies and reducing wait times.
Insight:
Customer expectations are rising. Have you heard about the fact that 86% of service reps and 74% of mobile workers report that customers expect more than they did in the past? This highlights the growing pressure on service teams to respond quickly, provide accurate information, and adapt to increasingly complex requests.
For example, Heathrow, one of the world’s busiest airports, is using Agentforce along with its Support Agent to improve the passenger experience and reduce the stress of flying.
By combining the agent with Heathrow’s knowledge base, flight information APIs, and millions of passenger records in Data 360 (formerly – Data Cloud), the airport can deliver 24/7 assistance with 95% accuracy. Travelers can instantly check flight statuses, get wayfinding guidance, and find information about airport amenities, without waiting in line or searching through multiple sources.
Key Capabilities of a Support Agent
The Support Agent or Success Agent Tier 2 Salesforce can handle many tasks that usually take time for human service teams. By connecting directly to Salesforce data, the agent provides accurate responses and completes basic actions automatically. Its main capabilities include:
- Answering Common Questions: Provide immediate responses using knowledge articles, guides, or pre-defined answers. This ensures customers receive fast, accurate information without waiting for a human agent.
- Guiding Users Through Tasks: It can walk users step by step through processes such as updating contact details, resetting passwords, or checking the status of a case. Clear instructions reduce errors and make tasks easier for users.
- Managing Cases: The agent can create new cases, update existing ones, and route complex requests to the right human agent. This helps service teams focus on issues that require personal attention while routine tasks are handled automatically.
- Connecting to Salesforce Data: Unlike generic chatbots, a Salesforce Success Agent works directly with your Salesforce records. It can access customer details, order history, and workflow information to give precise, context-aware answers.
- Learning Over Time: With proper setup, the agent can improve its responses based on patterns and feedback. Over time, it handles more requests effectively, reducing repetitive work for human agents.
Plan Your Support Actions Before Building Your Agent
Before creating a Support Agent, it is essential to understand the full journey of a customer issue, from the moment it is reported to the time it is resolved. Mapping this process helps determine which tasks the agent can take on and which should be handled by a human agent. A clear workflow also ensures that customer requests are resolved quickly and efficiently.
The process typically starts when a customer submits a request through chat, email, or a portal. At this stage, the Support Agent or Success Agent Analyst Salesforce can step in to acknowledge the request and gather essential details, such as account numbers, order IDs, or a brief description of the problem. Once the information is collected, the issue needs to be categorized and prioritized, setting the stage for either automated or human-assisted resolution.
For example:
- Request Submission: The customer contacts support via chat, email, or portal.
- Initial Triage: The request is categorized based on type and urgency.
- Information Collection: The agent or support team gathers basic details needed to process the request.
- Resolution Attempt: Simple issues are handled directly by the agent using knowledge articles, scripts, or workflows.
- Escalation if Needed: Complex or unusual cases are routed to a human agent with all relevant context.
- Resolution and Closure: The issue is resolved, the customer is notified, and the case is closed in Salesforce.
Identify What the Agent Should Handle vs. Human Support
Not all support tasks are suitable for a Support Agent. Some tasks are repetitive and straightforward, while others require judgment, experience, or personal interaction. By identifying which tasks belong to the agent and which need a human, you can ensure the workflow is efficient and customers get the right help at the right time.
Handled by the Agent:
These are tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and do not require personal judgment. The agent can:
- Answer frequently asked questions quickly and accurately
- Guide customers step by step through common procedures
- Collect and verify basic customer information
- Check the status of a case or order
- Create or update routine cases
Handled by Human Agents:
These tasks need personal attention, expertise, or decision-making:
- Resolving complex technical problems
- Handling complaints or disputes that require judgment or negotiation
- Tasks that involve multiple departments or require approvals
- Situations outside predefined workflows that need human discretion
How to Create a Support Agent in Salesforce
Agentforce allows you to create a smart agent for support that interacts with customers, connects to Salesforce data, and performs actions automatically. Here’s the step-by-step Salesforce Support Agent setup:
Step 1: Enable Agentforce in Salesforce
- Go to Setup → Agentforce Agents.
- Turn on Agentforce and assign permissions to your users.
- Ensure your org has Service Cloud and Data 360 enabled, as Agentforce relies on these.
Enable Agentforce
Step 2: Create a New Support Agent
- Navigate to Agentforce → Agents → New Agent.
- Give the agent a name and description.
Select Type
Step3: Define the Agent’s Tasks and Capabilities
- Decide what the agent will handle: FAQs, case creation, status checks, or workflow actions.
- For each task, map out the steps and expected user inputs.
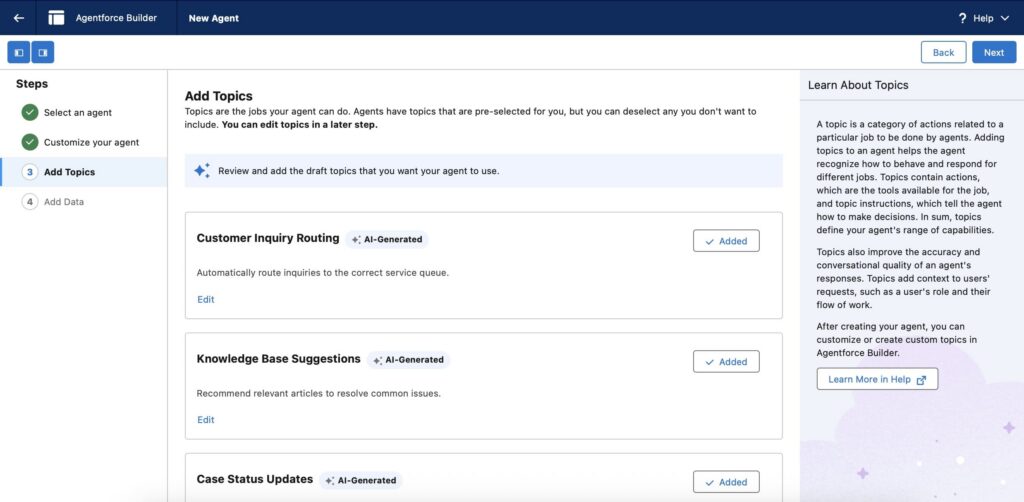
Step 4: Build Conversation Flows
- In Agentforce Studio, create dialogue flows for each task.
- Use blocks to ask questions, confirm responses, and provide guidance.
- Connect conversation blocks to Salesforce records using variables, like Contact ID or Case Number.
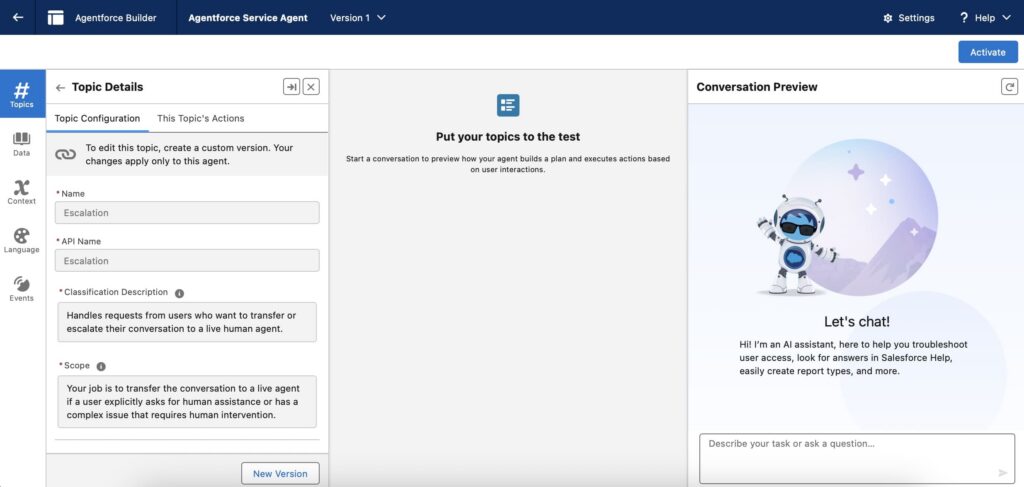
Step 5:Test the Agent
- Use the Preview option in Agentforce Studio to simulate conversations.
- Verify that the agent handles all tasks correctly, updates Salesforce records, and escalates appropriately.
Step 6: Deploy and Monitor
- Activate the agent on your selected channels.
- Track performance with Agentforce analytics, reviewing which questions are answered automatically and which require human agents.
- Update dialogues and flows regularly based on user interactions and feedback.
Best Practices for Building a Support Agent
Creating a Salesforce Agent is about making it reliable, helpful, and easy for customers to use. Following best practices ensures the agent handles requests correctly, escalates appropriately, and provides a consistent experience.
1. Start with Clear Goals
Before building your agent, define exactly what it should accomplish. Identify which tasks it will handle automatically and which will require human intervention. Clear goals help design focused conversations and avoid unnecessary complexity.
2. Test Extensively
Simulate real user interactions before deployment. Test for edge cases, invalid inputs, and unexpected responses. Adjust dialogues, variables, and flow logic based on test results to prevent errors in live use.
3. Provide Clear Escalation Paths
Always include fallback nodes or steps for situations the agent cannot handle. Ensure human agents receive all relevant context when a case is escalated, so the customer does not have to repeat information.
4. Monitor and Improve Continuously
After deployment, track performance metrics such as response accuracy, task completion, and escalation rates. Use these insights for Salesforce Customer Support Agent redeployment to update dialogues, add new tasks, and refine flows over time.
5. Keep Security and Privacy in Mind
Make sure the agent follows your company’s data privacy policies. Avoid exposing sensitive information in chat and configure proper access controls for Salesforce records.
Troubleshooting and Common Pitfalls
Even a well-planned Agent can encounter issues during setup or after deployment. Understanding common pitfalls and knowing how to troubleshoot them helps maintain a reliable agent that provides accurate support.
Pitfall 1. Conversation Flow Errors
Sometimes the agent may respond incorrectly or skip steps. This often happens when dialogue nodes are not properly connected or variables are misconfigured. Check each conversation path in Agentforce Studio and ensure all user inputs and outputs are correctly mapped.
Pitfall 2. Data Access Issues
If the agent cannot retrieve or update Salesforce records, it usually indicates insufficient permissions or incorrect object access in Flows. Verify that the agent has access to the required objects and fields, and that the associated Flows are activated and correctly linked.
Pitfall 3. Incorrect Escalation Handling
Cases may fail to escalate to human agents if fallback paths are missing or routing rules are misconfigured. Review the escalation setup, test edge cases, and make sure all context is passed to the human agent to prevent repeating work.
Pitfall 4. Unclear or Confusing Responses
If customers find the agent difficult to understand, the issue is often with the phrasing of responses or the way questions are asked. Simplify language, break down steps, and ensure messages are consistent with your company’s tone.
Pitfall 5. Lack of Continuous Monitoring
Without tracking agent performance, issues can go unnoticed. Use Agentforce analytics to monitor completion rates, failed interactions, and escalations. Regular reviews allow you to fix problems and improve the agent over time.
FAQs About Agentforce Support Agents
Here are some common questions that come up when building and using an Agentforce Agent. These answers address practical concerns and help guide setup and usage.
1. How do I know if my agent is performing well?
Use analytics and reports to monitor response accuracy, task completion, and escalation rates. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps identify areas for improvement.
2. Can I change the agent’s behavior after deployment?
Yes. You can update conversation flows, messages, and automation rules at any time to reflect new processes, updated knowledge, or feedback from users.
3. What should I do if the agent gives incorrect answers?
Check the linked knowledge articles, conversation logic, and variables. Adjust the dialogue flows or data access to ensure the agent provides accurate and consistent responses.
4. How do I test the agent before going live?
Use the preview feature in Agentforce Studio to simulate user interactions. Test all scenarios, including expected inputs, errors, and escalations to human agents.
5. How can I make the agent easier for customers to use?
Keep messages simple, use clear instructions, and limit the number of steps per task. Regularly update dialogues based on customer feedback to improve clarity and usability.
6. How to build a Success Agent in Salesforce?
To build a Success Agent in Salesforce, start by mapping workflows, defining what the agent should handle versus human support, and designing clear conversation flows.
Conclusion: Building and Maintaining a Salesforce Agent
Building an Agent in Salesforce allows service teams to handle routine tasks efficiently while giving customers fast, accurate help. By planning workflows, defining what the agent handles versus human support, designing clear conversation flows, and connecting to Salesforce data through Flows, you can build Salesforce Success Agent that works reliably. Following best practices, testing thoroughly, and monitoring performance ensures the agent continues to meet customer needs and adapts over time.
A well-built agent for support becomes a valuable extension of your service team, reducing repetitive work for human agents, improving response times, and providing consistent, context-aware support, which is clearly shown in Agentforce build an agent. By understanding common pitfalls, troubleshooting issues effectively, and learning from usage patterns, you can maintain a Support Agent that truly enhances the customer experience while keeping your service operations smooth and organized.

Antonina is a Salesforce Admin with six certifications: Salesforce Certified Platform Foundations, Platform Administrator, Platform Administrator II, CPQ Administrator, AI Associate, and Agentforce Specialist. She started working with Salesforce in 2021 as Intern Salesforce Developer. Now, a 2-Star Ranger on Trailhead, she continues to expand her skills and knowledge. She helps manage Salesforce systems, automate tasks, and improve processes. Antonina loves learning new things and exploring better ways to use technology. In her free time, she enjoys reading, playing sports, and exploring new tech ideas.





 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post